7 Things That Cause the Elderly to Fall
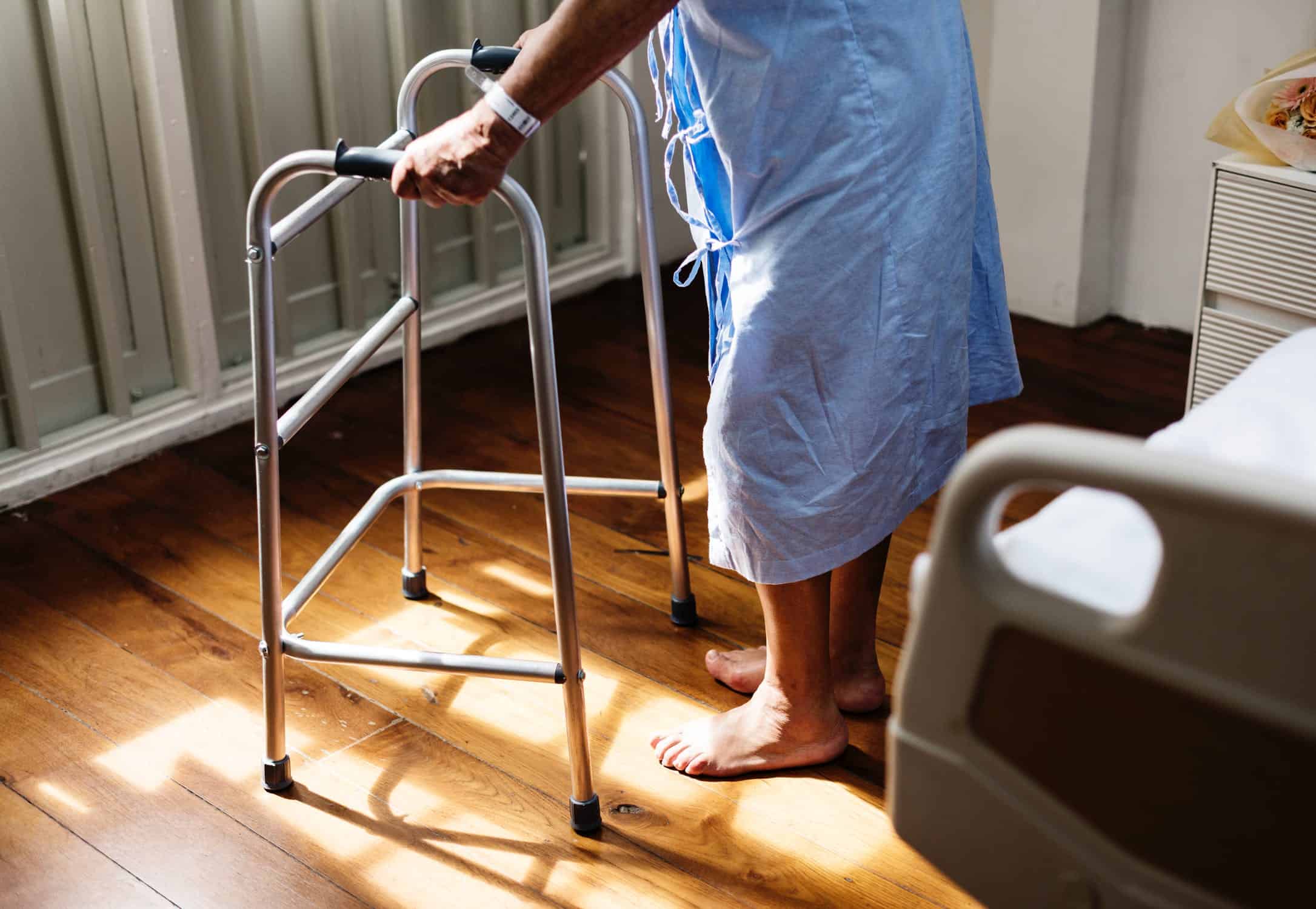

Falls are the leading cause of death, injury and hospital admissions among the elderly population. According to the National Council on Aging (NCOA), one out of every four Americans aged 65 and older falls every year.
Not only are seniors more prone to falling, but they are also more susceptible to fall-related injuries such as a broken hip or head trauma. Understanding why older individuals are at an increased risk can help family caregivers take the proper precautions to keep their loved ones safely on their feet.
Several factors contribute to the fact that seniors fall so much more frequently than younger people.
What Causes Elderly People to Fall?
- Decline in Physical Fitness. Many adults become less active as they get older, which exacerbates the physical effects of aging. Failure to engage in even mild exercise on a regular basis results in reduced muscle strength, decreased bone mass, loss of balance and coordination, and reduced flexibility.
- Impaired Vision. Age-related eye diseases can make it difficult, if not impossible, to detect fall hazards, such as steps, puddles and thresholds. Even if a senior is in top physical condition, failing to see obstacles or changes in ground level can lead to a nasty tumble. Refusing to follow physician recommendations for treatment, including wearing eyeglasses and using necessary low vision equipment can lead to a fall as well.
- Medication. A wide variety of medications can increase a senior’s risk of falling. Side-effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness and low blood pressure, can all contribute to an accident. Sedatives, anti-depressants, anti-psychotics, opioids and some cardiovascular drugs are the most common culprits. According to the Merck Manual, just over 40 percent of seniors take at least five drugs per week. Taking multiple medications increases the risk of medication interactions and falling. Keep in mind that over-the-counter medications and supplements can have powerful side effects and synergistic effects, too.
- Chronic Diseases. Health conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and arthritis cause weakness in the extremities, poor grip strength, balance disorders and cognitive impairment. Poor physical health increases a person’s initial risk of falling and minimizes their ability to respond to and recover from hazards, like tripping or slipping. Peripheral neuropathy, or nerve damage, can cause numbness in the feet, making it very difficult for a senior to sense environmental hazards and get around safely.
- Surgical Procedures. Hip replacements and other surgeries can leave an elderly person weak, in pain and discomfort, and less mobile than they were before the procedure. This can be temporary while a patient heals or a new and lasting problem.
- Environmental Hazards. The majority of falls in the elderly population occur in or around seniors’ homes. Environmental factors such as poor lighting, clutter, areas of disrepair, loose carpets, slick floors and lack of safety equipment can jeopardize a senior’s safety in their home.
- Behavioral Hazards. A person’s fall risk is influenced by their unique lifestyle and behaviors. This includes the types of activities they engage in, the level of physical demand these activities require, and their willingness and ability to adapt their routine for enhanced safety. For example, laundry is a normal daily activity for many people, but it can involve a great deal of exertion for a senior, especially if they transport a heavy laundry basket. This can be risky on its own, but if they also refuse to wear secure, non-skid footwear or attempt to navigate stairs, they put themselves at greater risk. Failing to modify behaviors to account for new or increasing difficulties is a serious, yet common, contributing factor for falls in older individuals.
A fall rarely occurs due to only one of the reasons above. When any of these factors combine, it can lead to a serious, possibly life-threatening injury. Even if a loved one is lucky to escape a fall uninjured, the experience can leave them shaken. The fear of falling again can cause them to withdraw and become more sedentary, which often leads to further physical and even mental decline. To keep your loved one safe and healthy, learn how you can modify their home and lifestyle to prevent fall-related injuries.
Resource: AgingCare. 7 Things That Cause the Elderly to Fall.
Recent Posts
Social Media for Older Adults: A Guide for Seniors
Social media is a helpful tool for seniors looking to stay connected with family and… Read More
The Best Exercises for Seniors
No matter your age, exercising regularly offers countless benefits. Exercise is key to a healthy… Read More
Thoughtful Gift Ideas for Assisted Living Residents
Giving a gift to a loved one in an assisted living community can brighten up… Read More
Downsizing Tips for Seniors: Helping Mom and Dad Move
Downsizing for retirement can be a big task, and many families come together to help… Read More
Senior Living Options: Homes and Apartments
Retirement isn’t one-size-fits-all, and neither are senior living options. Whether you buy or rent, want a… Read More
Tips for an Easier Transition into Assisted Living
If you’ve started to notice a decline in the mental or physical health of a… Read More

